IV Therapy for Insomnia: Safety, Process, and Realistic Results
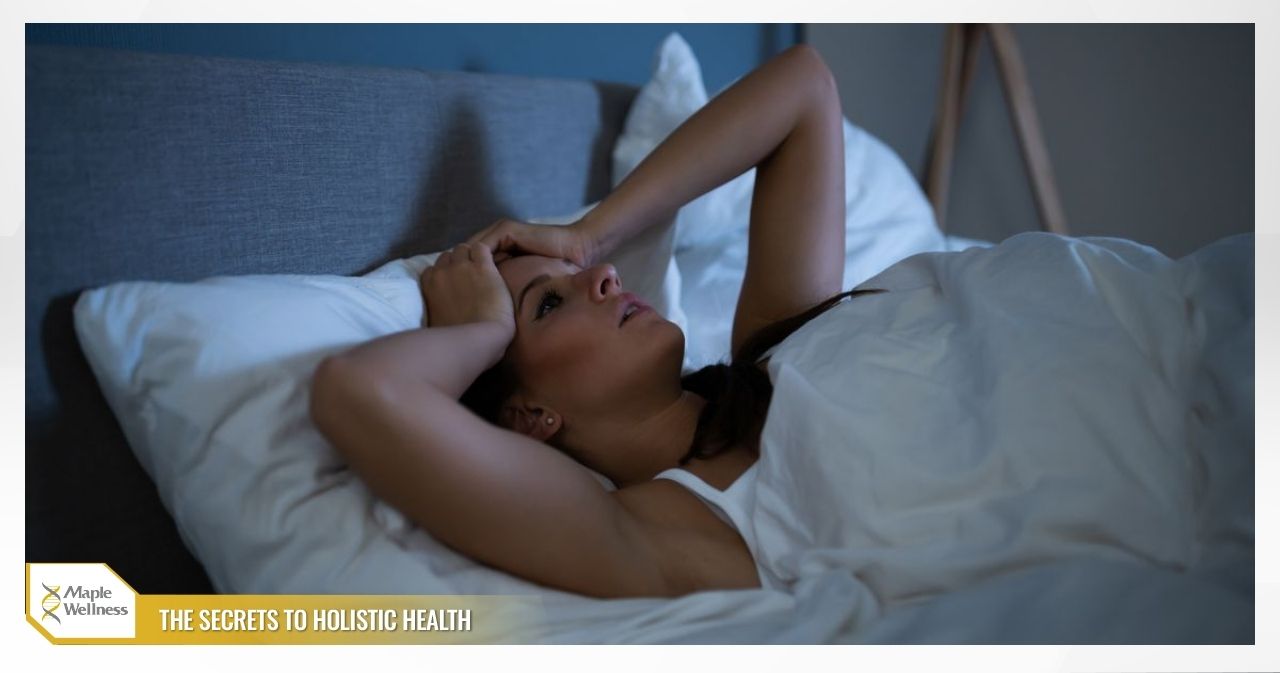
Insomnia disrupts normal sleep and blocks proper recovery. It can involve trouble falling asleep, repeated waking, or mornings of heavy fatigue. Many people with insomnia describe poor concentration, reduced work output, irritability, and lowered immunity. Ongoing sleeplessness often leads to heart disease, metabolic disorders, and depression. Doctors generally recommend behavioral therapy and structured routines as first-line approaches before considering treatments such as IV therapy for insomnia.
Where IV Fits in Your Sleep Plan
Start with Proven Basics: CBT-I and Routine
Clinicians describe insomnia as ongoing trouble with sleep that persists despite time in bed. Sleep-onset insomnia means taking more than 30 minutes to fall asleep. Sleep-maintenance insomnia means frequent awakenings or early rising. Non-restorative sleep means you clock hours yet wake still unrefreshed, drained, and unfocused the next day.
Daily habits shape sleep more than most people expect. Racing thoughts keep the brain on high alert when the lights go out. Irregular bed and wake times pull your body clock off schedule. Late screens suppress melatonin through bright blue light. Evening stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and some decongestants push sleep away. Alcohol may knock you out, but it fragments sleep later. A calm routine, dim light, and a cool room help your system power down gradually.
Clinical guidelines point to cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia, or CBT-I, as first-line care. Short courses of medication can help under a doctor’s care. Any add-on, including IV therapy for insomnia, belongs inside a plan that addresses habits and stressors. Work with a clinician who can tailor steps, measure results, and adjust.
Nutrients That Matter for Sleep
Certain nutrients influence the chemistry that sets your sleep-wake rhythm. Vitamin B6 helps convert tryptophan into serotonin, then into melatonin. When B6 runs low, mood can dip and sleep timing can drift. Balanced intake supports steadier cycles and smoother transitions between stages of sleep at night.
Magnesium deserves attention. It regulates nerve signals and helps muscles relax, helping the body prepare for rest. Low magnesium levels can increase nervous tension and reduce sleep depth. When combined with melatonin and B vitamins, supplementation has demonstrated stronger benefits than using one nutrient alone.
What Goes in the Drip
IV therapy for insomnia delivers vitamins and minerals directly into the bloodstream. Common formulas include magnesium, B-complex, and vitamin C in sterile fluids. The route bypasses digestion and raises circulating levels quickly. Evidence is still developing, so IV therapy for insomnia should never replace core care. Examples of such care include CBT-I and a solid medical routine. Teams personalize drips to your history and goals, then track response and adjust in follow-up visits.
Who It’s For, Who Should Skip It
Candidates After Screening
Not everyone with ongoing sleepless nights should receive intravenous support. Thorough screening comes first with a clinician who knows your history. Teams review insomnia patterns, medications, supplements, alcohol, caffeine, shift work, apnea signs, mood, allergies, and thyroid status. Labs may include magnesium, vitamin B12, vitamin B6, ferritin, and vitamin D. Testing helps confirm needs before any infusion plan.
Some patients seek short-term support during jet lag or high-demand periods when sleep tools are already in place. In these cases, IV therapy for insomnia may function as an adjunct rather than a cure. It fits inside a structured plan that addresses habits, timing, and stress. Clinicians personalize dosing to history and goals, then track response. If basics still carry gaps, the drip can provide targeted support for a limited window.
Safety Exclusions and Red Flags
Doctors advise against this method for people with uncontrolled high blood pressure, advanced kidney disease, heart failure, or arrhythmias. Active infection or severe anemia also raises risk. Pregnant or breastfeeding patients should avoid treatment because safety data remain currently uncertain. Potential risks to mother and child outweigh any possible benefit in this setting.
People with allergies to infusion components should avoid these formulas. Medication interactions, such as with diuretics, require review. Dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or fainting history warrants evaluation before considering IV therapy for insomnia.
Clinicians weigh benefits against risks when judging suitability. People with fragile veins, uncontrolled hypertension, or cardiovascular disease face complication chances. They may experience shifts in electrolytes or circulation, so teams recommend alternatives until stability is achieved.
Proper screening protects patients and guides decisions. When infusion is unsuitable, teams recommend options. Services still include IV for stress or sleep fatigue relief under supervision.
Benefits You Can Expect and Precautions That Protect You
At-Site Issues and How We Prevent Them
Any intravenous procedure carries small risks at the point of entry. You may feel a quick sting as the needle goes in. Bruising can appear, especially for people with fragile veins. The vessel wall can inflame, a condition called phlebitis. If irritation develops, the site may swell or feel warm. Nurses check for infiltration, where fluid slips into tissue outside the vein. Extravasation, a more serious leakage, can cause discomfort and needs prompt reassessment. These routine checks protect patients receiving IV therapy for insomnia.
Whole-Body Risks and Medication Interactions
Systemic effects may arise once fluids and nutrients circulate. Rapid infusion increases circulating volume and strains the heart and kidneys. People with cardiovascular disease or kidney impairment face higher risk of overload. Electrolytes can shift if solutions contain concentrated minerals. For example, magnesium infusion can drop blood pressure quickly. Rarely, hypersensitivity reactions appear as rash, itching, or dizziness. Careful pacing matters for IV therapy for insomnia.
Medications add complexity. People on diuretics or antihypertensives can experience changes in electrolytes or circulation during infusion. Clinicians at Maple Wellness review each patient’s history before planning IV therapy for insomnia to reduce risk. Questions about lifestyle, nutrition, and stress help refine the plan and provide a fuller picture.
Monitoring and Clear Stop Rules
Safety continues once infusion starts. Continuous observation prevents small issues from escalating. Nurses record vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature throughout therapy. They also check the infusion site every fifteen to thirty minutes to confirm the vein remains stable.
Clear stop rules guide the team. They pause infusion if pain spreads beyond the entry point or swelling appears. Redness or warmth around the insertion site signals inflammation. Dizziness or a sudden drop in blood pressure needs immediate action. Severe reactions, though rare, require discontinuation and medical support. In these situations, clinicians stop IV therapy for insomnia and stabilize the patient according to protocol.
At Maple Wellness, trained staff follow strict protocols to minimize risk. The team provides personalized plans, then monitors closely to catch adverse effects early. With this vigilance, therapies such as the better sleep IV support rest without compromising health. The structured approach helps patients feel confident that safety remains the central priority throughout the visit.
Your IV Session: Step by Step
Step 1 — Pre-infusion Screening
Every safe infusion starts with careful screening. Your doctor reviews your sleep history, medications, and current conditions. This step flags issues such as untreated sleep apnea, uncontrolled hypertension, or active infections. You may also answer questions about stress, caffeine, and daily routines. The conversation is collaborative and practical. If concerns appear, the doctor may guide you toward cognitive behavioral therapy first. Screening ensures IV therapy for insomnia remains appropriate only when clear criteria are met and when potential risks are addressed.
Step 2 — Targeted Micronutrient Testing
After the initial review, your clinician may order focused lab tests. Common checks include magnesium, vitamin B12, and vitamin D levels. Testing prevents indiscriminate supplementation that could cause imbalance. A targeted plan reflects actual needs rather than guesses. Clear targets make each ingredient purposeful and safer. Baseline numbers also help with later comparisons. You and your team can then judge whether treatment produces measurable improvement over time.
Step 3 — Your Personalized Formula
The doctor studies your results and builds a plan for you. They select nutrient families to match goals such as stress support, hydration, or deficiency correction. You will hear the likely benefits and the possible risks. The physician also confirms informed consent. By tailoring the approach, Maple Wellness ensures IV therapy for insomnia complements existing care rather than replacing it. This process feels personal and transparent. Personalization helps you feel your therapy aligns with medical evidence and your needs.
Step 4 — Infusion and Active Monitoring
Nurses use sterile techniques during infusion to reduce infection risk. The solution flows at a measured rate that suits you. You stay under observation, and staff record vital signs at intervals. Nurses also check the cannula site to confirm the vein remains stable. If pain, swelling, or dizziness appears, the team adjusts or stops the infusion. Small adjustments keep you comfortable and safe. Ongoing monitoring protects your health and reassures you that care remains constant at every stage.
Step 5 — Aftercare and Follow-up
Care continues once the infusion ends. Your doctor may ask you to keep a sleep diary for two to four weeks. The record shows improvements and signals when changes are needed. A follow-up visit allows the doctor to review progress and answer questions. Ongoing oversight keeps safety front and center and clarifies the therapy’s role. IV therapy for insomnia works only as one part of a larger strategy. That strategy includes lifestyle habits and medical guidance. It keeps expectations realistic while you build better rest over time.
Food-First Alternatives and Lifestyle Upgrades
Daily Sleep Habits That Work
Good routines form the backbone of sleep health. People in midlife often juggle careers, family, and health changes. Consistent bedtimes reinforce circadian rhythm and improve predictability. Morning light resets the body’s clock and boosts alertness. Evening habits matter too. Avoid caffeine, nicotine, or heavy meals near bedtime because they stimulate digestion and the nervous system. Reducing late-night screens lowers blue-light disruption that otherwise delays melatonin release. These habits, together with IV therapy for insomnia, build a steadier base for recovery. Small, steady changes compound over weeks and make sleep improvements easier.
Infrared Sauna for Relaxation
Relaxation tools add support when stress keeps you wired. Short infrared sauna sessions may ease muscle tension and encourage calm before bed. Many adults say twenty minutes at moderate temperature improves circulation and relaxation. Hydration afterward helps restore balance. People with cardiovascular disease or unstable blood pressure should check with their doctor first. Safe practice keeps potential benefits without extra strain. When managed well, pairing sauna use with medical care and IV for stress may improve overall rest patterns. This approach creates a calming nightly routine.
Eat for Better Sleep: Magnesium, B-Vitamins, Tryptophan
Diet shapes sleep as much as daily routines. Magnesium-rich foods such as nuts, seeds, and leafy greens support neurotransmitters involved in relaxation. Whole grains, oily fish, and dairy also provide essential nutrients for nervous system balance. Adequate vitamin B12 and vitamin D help regulate circadian rhythm and mood stability. For many patients, oral supplements offer a gentler first step before infusion. Clinicians often recommend dietary upgrades even for those already receiving IV therapy for insomnia. A nutrient-dense plan keeps stores stable between sessions and creates conditions where medical support can work more effectively.
What to Expect: Onset, Frequency, Outcomes
How Soon You May Notice Effects
Some people notice better sleep within days, while others see smaller changes over several weeks. Results vary with health, nutrient status, daily habits, and routines too. A sleep diary helps you track changes objectively. Consistent entries reveal patterns and show whether IV therapy for insomnia truly helps. Short-term gains are possible, yet durable progress depends on a full plan with daily habits and medical guidance.
Session Frequency and Course Length
Clinicians emphasize moderation. One infusion rarely fixes complex insomnia. Most plans start with a single session and a careful review. Your doctor may schedule further sessions two to four weeks apart, depending on progress. Repeat only when documented benefits appear. Keep goals specific and measurable weekly. Overuse adds risk without extra reward. Your team guides timing so IV therapy for insomnia stays safe and purposeful. Remember that healthy sleep grows gradually through steady practice, not quick fixes or unrealistic expectations.
When to Stop and Seek Care
Medical supervision keeps delivery safe, yet patients should stay alert to warning signs. Severe fatigue, leg swelling, or sudden chest discomfort needs immediate attention. Call your clinician or emergency services. Report local redness, sharp pain, or swelling around the infusion site right away. Do not ignore dizziness or shortness of breath. Maple Wellness advises stopping the infusion at the first sign of distress. That vigilance protects safety while preserving potential benefits. The better sleep IV can help during demanding periods, but only under close guidance from trained clinicians.
Choosing the Right Tool: IV vs Oral vs CBT-I
Patients often compare infusion with tablets or behavioral care. IV therapy for insomnia sends nutrients into the bloodstream quickly. That can feel faster in the short term. Oral options such as magnesium or melatonin absorb through digestion. Their effects build more gradually. Both routes can support a plan when chosen with care.
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia remains the strongest long term solution. It retrains patterns that keep the brain alert. The method takes coaching and practice, yet outcomes endure. Many people pair oral nutrients with CBT-I. That approach supports circadian rhythm, mood, and steadier pre-sleep routines.
Used carefully, IV therapy for insomnia works best as an adjunct within a structured plan. Teams screen for deficiencies and review medications before any drip. Sessions may target short windows such as travel recovery or periods of stress. Your clinician guides sequence and timing so each step fits your goals.
FAQs (People Also Ask)
1. Does IV therapy help with insomnia?
It can help briefly; some patients use IV for stress under clinician guidance.
2. How long do effects last?
Results vary. Many report benefits for several days, not weeks.
3. How many sessions are safe per month?
Most people stay within two sessions monthly, adjusted after evaluation.
4. Is IV safe if I have high blood pressure or kidney disease?
No. These conditions raise risk, so clinicians recommend safer alternatives.
5. IV vs melatonin or magnesium pills: which first?
Start with oral options such as melatonin or magnesium. Add infusion only if deficiencies persist.
6. Can “better sleep IV” replace CBT-I or sleep meds?
No; IV therapy for insomnia does not replace CBT-I or prescribed medication.
7. What are the common side effects of IV therapy for insomnia?
Common effects include bruising, dizziness, mild swelling, and blood pressure drops.
8. What screening do I need before my first IV?
Doctors review history and medications, and may order targeted blood tests.
9. Can IV vitamins interact with my medications?
Yes. Diuretics and antihypertensives can interact, so doctors review prescriptions.
IV therapy for insomnia can support sleep goals when it sits inside a complete care plan. Maple Wellness emphasizes careful screening, steady monitoring, and clear aftercare. Patients feel confident knowing each step protects well-being while addressing persistent sleep concerns with measured, practical care. Feel free to reach out for consultation here: MAPLE HEALTHCARE FANPAGE.
Related articles:
MAPLE INTERNATIONAL CO., LTD
Phone: 0705 100 100
Tax code: 0311948301
Date Range: 21 - 08 - 2012
Issued: Department of Planning and Investment of Ho Chi Minh City